Alignment Validation
The alignment validation tool allows to load into Semantic Turkey ontology alignment documents expressed according to model of INRIA's Alignment API and to validate them. The results of the validation can then be re-exported in the same format and/or transformed into plain OWL/SKOS mapping triples and loaded into the project's dataset.
The Alignment Validation tool can be accessed from the ST toolbar.
The UI of the tools is quite simple, it allows to select and load an alignment file stored into the filesystem. This tools can handle rdf/xml alignment files compliant with INRIA Alignment format.
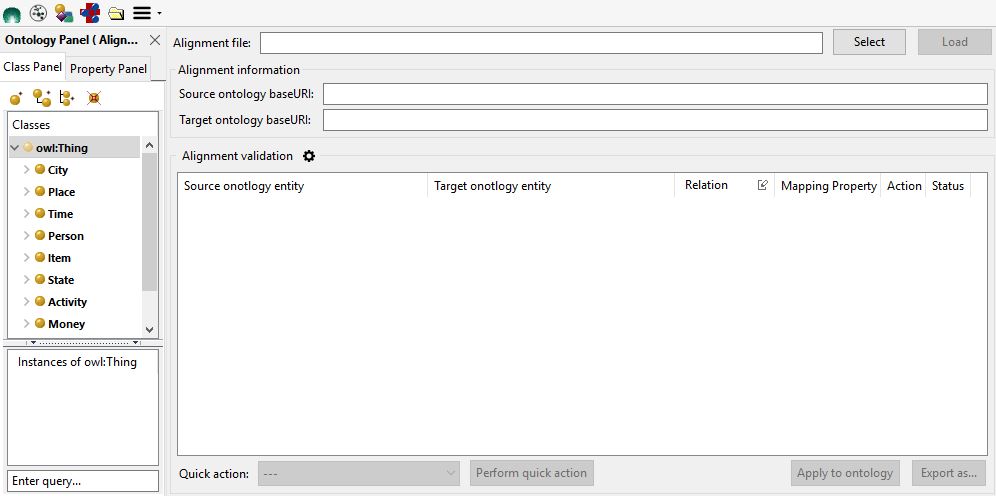
The tool is able to recognize, through the baseURI of the two aligned ontologies, which one is the source ontology (the ontology currently loaded in Semantic Turkey) and which one is the target. If none of the baseURIs of the aligned ontologies corresponds to the baseURI of the local ontology, an error message will be prompted.
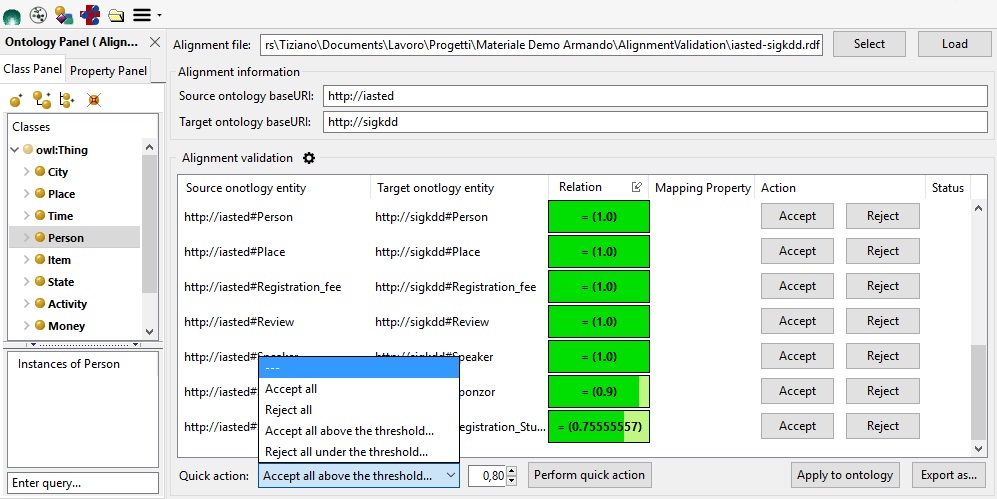
The images in this page show the process of validating alignments between the Iasted ontology, loaded in ST, and the Sigkdd ontology. The ontologies and alignment files are downloadable from the conference track of OAEI 2013.
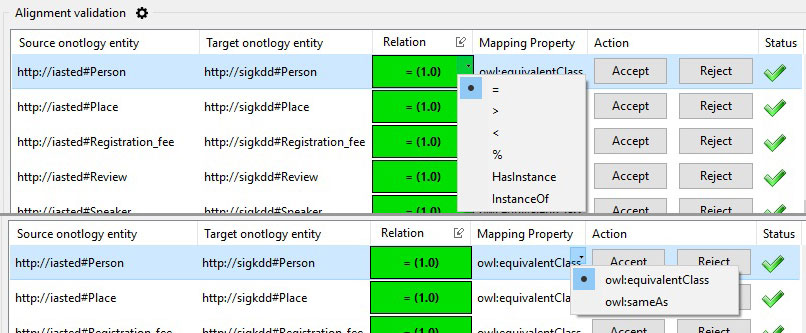
Once the alignment file has been loaded, the tool shows a table with the alignments to be validated. Each row reports the source and target resource to align, the proposed alignment relation together with a measure representing the confidence of the alignment, and two buttons allowing the user to accept or reject the proposed alignment. Two further columns are automatically filled by the system:
- Mapping Property. The cells in this column suggest a mapping property from the OWL or SKOS vocabularies to be used for the proposed alignment. This property depends on the mapping relation proposed for the alignment (e.g. a ">" relation between two skos concepts would result in proposing a
skos:broaderMatchmapping property among them) and is computed by the system only after an alignment is accepted. The property can then be modified by the user; - Status. This column reports, by means of an icon, the status of the alignment. There are three status marks: accepted
 , rejected
, rejected  and error
and error  . This last status is applied when the relation between the two aligned resources cannot be asserted for some reason (for instance, due to the types of the involved resources and the mapping property being proposed, e.g. two classes related with hasInstance).
. This last status is applied when the relation between the two aligned resources cannot be asserted for some reason (for instance, due to the types of the involved resources and the mapping property being proposed, e.g. two classes related with hasInstance).
- Accept all: mark as accepted all the alignments;
- Reject all: mark as rejected all the alignments;
- Accept all above the threshold: mark as accepted all the alignments with the relation measure higher than the given threshold;
- Reject all under the threshold: mark as rejected all the alignments with the relation measure lower than the given threshold;
As explained before, accepting an alignment could result in an error message if the relation between the aligned resource cannot be asserted.
The tool allows users to customize two validation aspects in a sequential order: by first, the alignment relation can be changed among the set of relations available in the INRIA's Alignment format, the mapping property can then be selected accordingly (i.e. the mapping property must implement the relation asserted in the INRIA's format and be compatible with the types of the aligned resources).
The changes brought by the user can be exported in a new RDF file in order to save a snapshot of the validation process and reload it at a later time.
Note that the exported alignment file now complements the Alignment format with added custom information: the mappingProperty and the status attributes, detailing the information specified by the user during the validation process.
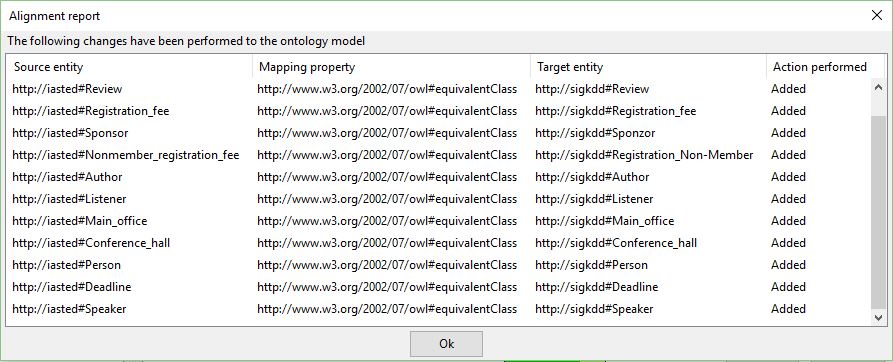
As an alternative to the export, the user can project the validated relationships into plain mapping triples (adopting the standard mapping properties identified in the "Mapping Property" column) and assert them into the dataset being edited in the current project, by simply depressing the Apply to the ontology button. Then the tool adds to and removes from the ontology the triples corresponding respectively to the accepted and rejected alignments. A report is then prompted to the user, as in the following figure.
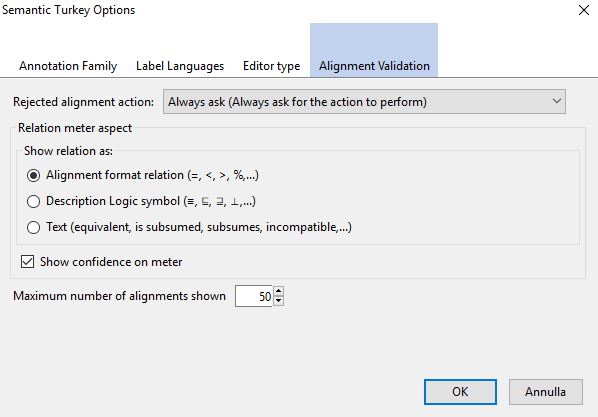
The tool offers a few configuration options available through the option panel (figure below). The option panel can be accessed through the "gear" button  on top of the alignment view or from the options button of the Semantic Turkey extension in the addons page of Firefox (see here). Through the option panel, the user can change the relation meter aspect (Relation column), the maximum amount of alignments shown and the action to perform on the rejected alignments when they are applied to the working ontology.
on top of the alignment view or from the options button of the Semantic Turkey extension in the addons page of Firefox (see here). Through the option panel, the user can change the relation meter aspect (Relation column), the maximum amount of alignments shown and the action to perform on the rejected alignments when they are applied to the working ontology.
FAQ
- Q: Despite the baseURI of the ontology loaded in ST matches the baseURI of one of the aligned ontology in the alignment file, the tool fails to load the alignment file with the error "Alignment file loading error: Failed to open and validate the given alignment file. None of the two aligned ontologies matches the current project ontology"
A: Probably the alignment file contains an error. The most common is a missing # at the end of the Alignment namespace, e.g. http://knowledgeweb.semanticweb.org/heterogeneity/alignment#
- Q: The tool fails to load the alignment file with the error "STException: java.io.IOException: org.openrdf.rio.RDFParseException: unqualified attribute '...' not allowed"
A: Probably the alignment file is an XML file, not RDF. INRIA's Alignment API allow for the possibility to generate XML Alignment files which are however not valid RDF.



